cJun Program Overview
Our cJun program is currently in lead optimization in preparation for nomination of a clinical candidate to move into IND-enabling studies. BioAce has a library of SPEAR candidates addressing cJun that inhibit the interaction with cFos and disrupt AP-1 complex formation, thereby inhibiting oncogenic activity. Initial data demonstrates in vitro cell killing and in vivo anti-breast cancer activity.
Target Overview – Jun/AP-1 Transcription Complex
Activator protein 1 (AP-1) is a transcription complex comprised of Fos and Jun protein subunits, and is involved in a wide range of cellular processes including proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. AP-1 is primarily regulated at the level of both Jun and Fos gene transcription by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and by post-translational modification via phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Dysregulation of the AP-1 complex drives the expression of oncogenic factors such as cyclin D, E2F and DP1, and has been observed in breast, ovarian, liver, skin, bone, lung, endometrial, and colorectal tumors, as well as many hematologic malignancies. Genetic inactivation of AP-1 in tumors inhibits tumor cell growth in vitro.
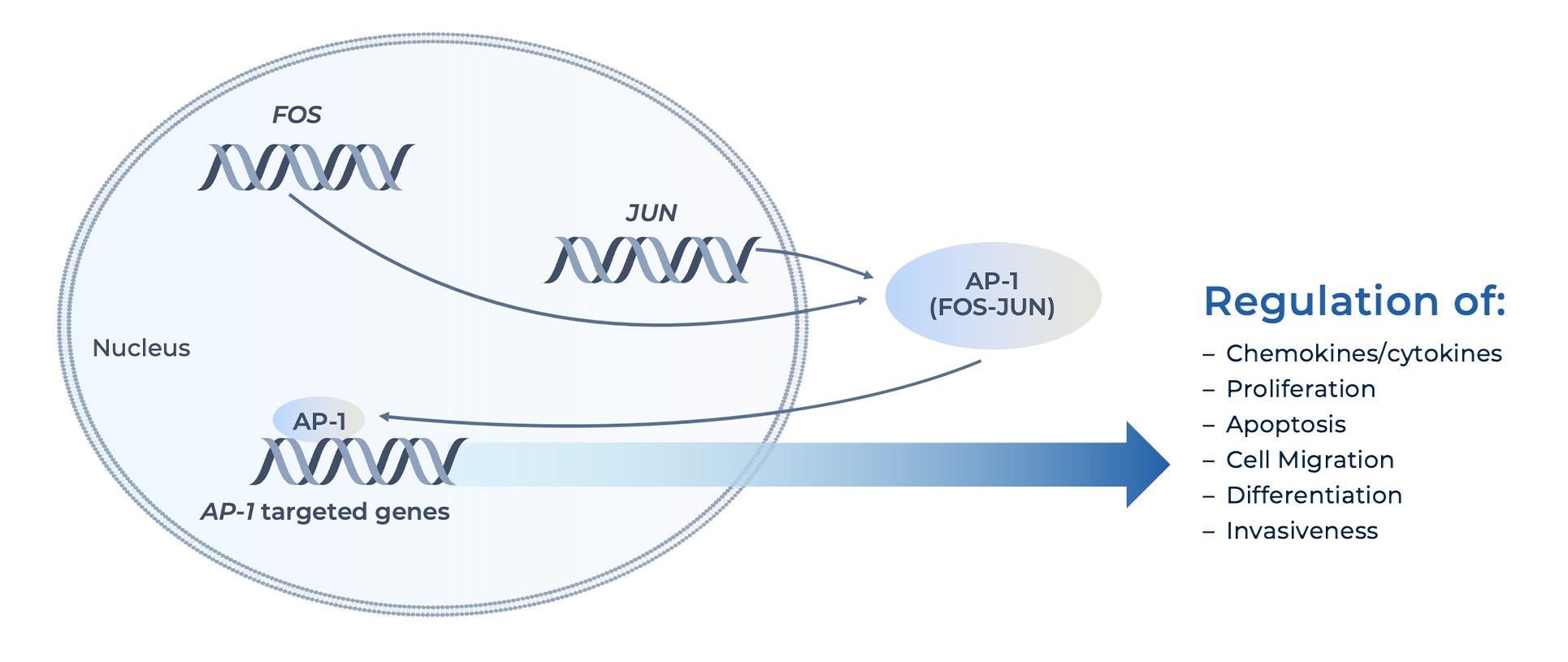
Image adapted from Nat Rev Cancer. 2003 Nov;3(11):859-68.
